Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maebara, Sunao; Ichikawa, Masahiro
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3284 - 3286, 2013/07
Maebara, Sunao; Ichikawa, Masahiro; Palmieri, A.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3287 - 3289, 2012/09
Umemori, Kensei*; Enami, Kazuhiro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Sato, Masato*; Shinoe, Kenji*; Sawamura, Masaru; Cenni, E.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.67 - 69, 2012/07
The Compact ERL, which is a test facility of ERL, is under construction in Japan. For the main linac, one cryomodule, containing two 9-cell superconducting cavities, is under development. Thermal design and cavity alignment have been also carefully considered. Two 9-cell cavities were already fabricated and their performances were confirmed by vertical tests. Their accelerating field reached to 25 MV/m, without field limits. Two input couplers, three HOM absorbers and two Slide-Jack tuners are also under fabrication for the cryomodule. High power processing will be applied for input couplers, at a test stand using a 300 kW klystron. Cooling tolerance and HOM damping abilities were tested for HOM absorbers. Some performance studies were also applied for the tuner at room temperature condition. Cryomodule assembly is planned on this summer. After cooling tests and high power tests will be carried out, ERL beam operation will be started.
Umemori, Kensei*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Sato, Masato*; Shinoe, Kenji*; Sawamura, Masaru; Cenni, E.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.2227 - 2229, 2012/07
The Compact ERL project, which is a test facility of ERL, is ongoing in Japan. At the first step of this project, main linac cavities accelerate electron beams by 30 MV. Two 9-cell cavities were fabricated for main linac cryomodule. A series of surface treatments were applied for the cavities. For the final EP, current density was selected to be relatively low. Vertical tests were performed for both cavities. Their field successfully reached to 25 MV/m, without any field limitation. The Q-values were more than 1 10
10 , even at 20 MV/m. Field emission on-sets were to be 14 and 22 MV/m, for each cavity. Both cavities satisfied requirements for ERL main linac cavity. Details of vertical tests, with X-ray and temperature mapping data, are shown, in this paper.
, even at 20 MV/m. Field emission on-sets were to be 14 and 22 MV/m, for each cavity. Both cavities satisfied requirements for ERL main linac cavity. Details of vertical tests, with X-ray and temperature mapping data, are shown, in this paper.
Cenni, E.*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Umemori, Kensei*; Shinoe, Kenji*; Sato, Masato*; Sawamura, Masaru
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.295 - 297, 2012/07
In order to develop the energy recovery linac at KEK, we are studying the performance of L-band superconducting cavities by means of vertical tests. One of the limiting factor for the cavities performance is power losses due to field emitted electrons. With regard to this phenomena a particle tracking code is used to study electron trajectories and deposited energy on the inner surface of the cavity. Different emitters location were tested within a range of accelerating field and phases in order to reproduce different scenario. The final goal of this study is to locate the sources of the electrons inside the cavity through a deeper understanding of the phenomena. To validate the results from the simulation the outcome data are compared with other particle tracking codes.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Kojima, Toshiyuki; Narita, Takahiro; Sakaki, Hironao; Komukai, Satoshi*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3972 - 3974, 2012/07
Control System for LIPAc realizes the remote control and monitoring and data acquisition by use of EPICS. For the validations of each subsystem performance and the activity of IFMIF Accelerator design, it is very important data obtained by commissioning of LIPAc and each subsystem. To certainly archive the important data for LIPAc and to efficiently search the LIPAc data, for design and validation, we started developing Data Acquisition System (DAC) based on Relational Database (RDB) has been developed. The first design for DAC of LIPAc is configured (1) using PostgreSQL for RDB and (2) several RDB for data archiving to ensure the data archive performance and to consider the increasing data amount. In addition, (3) only one RDB for data search is included in DAC and users can search the data via this RDB. In this way, several RDB for DAC can behave only one RDB against users. In this article, the development status of DAC for LIPAc is presented.
Hatakeyama, Shuichiro
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.843 - 845, 2012/05
Generally in the synchrotron, the frequency of transverse oscillation of the bunched beam for each single turn (usually called betatron tune or just "tune") is one of fundamental controllable knobs to avoid the instability of the accelerator. In this report, it is not mentioned about the effect to the beam instability but it is focused to various methods to measure the betatron tune by using bunch-by-bunch transverse beam position. The following items will be presented, (1) least square fitting to the time-domain beam position at specific location. (2) peak finding of the frequency-domain beam position at specific location. (3) phase space analysis of the beam position at specific location. (4) frequency-domain analysis of the beam position in the normalized coordinate at many locations in the ring orbit. For the application to the real accelerator, data of the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) will be shown.
Soda, Hikaru*; Nakao, Masao*; Noda, Akira*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Ito, Kiyokazu*; Okamoto, Hiromi*; Yuri, Yosuke; Jimbo, Koichi*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.397 - 399, 2012/05
Noda, Akira*; Nakao, Masao*; Soda, Hikaru*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Ito, Kiyokazu*; Okamoto, Hiromi*; Osaki, Kazuya*; Yuri, Yosuke; Jimbo, Koichi*; Grieser, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.394 - 396, 2012/05
 -ray source by compressed Nd:YAG laser pulse
-ray source by compressed Nd:YAG laser pulseDaito, Izuru; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Hayashi, Yukio; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Hajima, Ryoichi; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.4124 - 4126, 2012/05
A non-destructive detection system of nuclear material hidden in cargo containers is under development in JAEA and Kyoto University. The system is able to detect and identify isotopes of special nuclear material in a container by employing Nuclear Resonance Fluorescence triggered by mono-energetic laser Compton scattered  -ray. One of the most important technologies for such system is generation of
-ray. One of the most important technologies for such system is generation of  -rays at a flux of 3
-rays at a flux of 3 10
10 photon/s. In order to achieve this
photon/s. In order to achieve this  -ray flux with a compact system, a pulse compression system for Nd:YAG laser by using stimulated brillouin scattering has been developed. The laser pulse with a duration of 10 ns from a Nd:YAG laser is compressed down to 200 ps. As a feasibility study of the proposed system 400 keV
-ray flux with a compact system, a pulse compression system for Nd:YAG laser by using stimulated brillouin scattering has been developed. The laser pulse with a duration of 10 ns from a Nd:YAG laser is compressed down to 200 ps. As a feasibility study of the proposed system 400 keV  -ray generation is performed at KPSI by using 150 MeV electron beam from microtron accelerator and compressed Nd:YAG laser. Experimental results of pulse compression and
-ray generation is performed at KPSI by using 150 MeV electron beam from microtron accelerator and compressed Nd:YAG laser. Experimental results of pulse compression and  -ray generation are presented.
-ray generation are presented.
Yuri, Yosuke; Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Ishibori, Ikuo; Okumura, Susumu
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.1062 - 1064, 2012/05
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Schnase, A.; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Ezura, Eiji*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Takagi, Akira*; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.2952 - 2954, 2012/05
In J-PARC RCS, the high intensity beam is delivered to the MR. The longitudinal beam emittance at the RCS extraction should be optimized to avoid the beam loss after the MR injection. In order to match the longitudinal emittance shape between the RCS and the MR, it is desirable to enlarge the longitudinal emittance during the RCS acceleration. We have performed the particle tracking simulation for the controlled longitudinal emittance blow up in the RCS.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Schnase, A.; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Shimada, Taihei; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3924 - 3926, 2012/05
For acceleration of high intensity proton beams in the J-PARC MR, beam loading compensation is important. In the MA-loaded RF cavity in the MR, which has a  -value in the order of 20, the wake voltage consists of the accelerating harmonic (
-value in the order of 20, the wake voltage consists of the accelerating harmonic (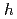 = 9) and the neighbor harmonics (
= 9) and the neighbor harmonics (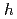 = 8, 10). We employ the RF feedforward method for the beam loading compensation, like in the J-PARC RCS, in which the impedance seen by the beam is greatly reduced by the feedforward. The full-digital feedforward system developed for the MR has a similar architecture to that of the RCS. The system compensates the beam loading of the important three harmonics (
= 8, 10). We employ the RF feedforward method for the beam loading compensation, like in the J-PARC RCS, in which the impedance seen by the beam is greatly reduced by the feedforward. The full-digital feedforward system developed for the MR has a similar architecture to that of the RCS. The system compensates the beam loading of the important three harmonics (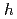 = 8, 9, 10). We present the structure of the RF feedforward system. Also, we report the preliminary results of the beam tests.
= 8, 9, 10). We present the structure of the RF feedforward system. Also, we report the preliminary results of the beam tests.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hayashi, Naoki; Hotchi, Hideaki; Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Saeki, Riuji; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Kato, Shinichi*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3901 - 3903, 2012/05
J-PARC Facilities were seriously damaged by the Great East Japan Earthquake in March 2011, but all facilities resumed a beam operation from December 2012. Beam commissioning results indicated that the beam loss and the residual dose at injection area in the RCS was reduced to 10% of before earthquake. This result owed to new collimator at injection area. The losses and residual doses of other area were almost same as before earthquake.
Kamiya, Junichiro; Ogiwara, Norio; Nishikawa, Masaaki; Hikichi, Yusuke; Yanagibashi, Toru; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.2522 - 2524, 2012/05
In the vacuum system of J-PARC Rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS), we use beam pipes and bellows whose materials are vacuum fired at 700 850
850  C in order to eliminate atoms in their bulk who are origin of outgassing. Until now, beam power has been increased up to 300 kW. Pressure in synchrotron beam line increased when the high power beam was accelerated. However, increment of pressure has reduced during the continuous beam operation. It is because the molecules, which adsorb on surface of the wall of the vacuum chambers, desorb by an ion bombardment and a heat generation due to an eddy current. Because the atoms in the bulk is eliminated, desorption of the molecules, which adsorb on the surface, means the reduction of the outgassing from the wall. In this presentation, we will report the past situation of the vacuum system during the beam operation. In addition, we also show the status after the Great East Japan Earthquake.
C in order to eliminate atoms in their bulk who are origin of outgassing. Until now, beam power has been increased up to 300 kW. Pressure in synchrotron beam line increased when the high power beam was accelerated. However, increment of pressure has reduced during the continuous beam operation. It is because the molecules, which adsorb on surface of the wall of the vacuum chambers, desorb by an ion bombardment and a heat generation due to an eddy current. Because the atoms in the bulk is eliminated, desorption of the molecules, which adsorb on the surface, means the reduction of the outgassing from the wall. In this presentation, we will report the past situation of the vacuum system during the beam operation. In addition, we also show the status after the Great East Japan Earthquake.
Hayashi, Naoki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hotchi, Hideaki; Kamiya, Junichiro; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tani, Norio; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamamoto, Masanobu; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3921 - 3923, 2012/05
The injection energy upgrade from 181 to 400 MeV for J-PARC RCS is planned in 2013. One power supply was replaced and using for a normal operation. An IGBT chopper type power supply which has larger switching noise will be changed to a capacitor bank type. New injection system allows the center injection with 400 MeV and switching painting area. As further steps for the leakage field, it begins to diminish the effect from the beam transport line. A quadrupole corrector system is designed and fabricated to compensate the beta beat due to the injection bump as the first step. Two profile monitors will be modified to correct position systematic errors and third one is going to be installed at dispersion free section. It is important to minimize kicker impedance lower, which may cause the beam instability. A diode, which has high reverse breakdown voltage and works with lower forward voltage, has been developed. Using this new diode, an experiment shows the impedance becomes lower.
Watanabe, Masao; Hayashi, Naoki; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Togashi, Tomohito; Toyama, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3629 - 3631, 2012/05
Stable operation is required for RCS at J-PARC. In the kicker system at extraction section of RCS, there had been many troubles for unstable operation of the thyratrons switches of the power supply just after 25 pps operation started in February 2009. However, the operation was improved by handling thyratrons in appropriate manner in October 2010. After the grate earthquake on 11 March 2011, injection and extraction magnets, power supplies, cables and bus-duct were checked. The results of the measurements and the checks were all not in the problem. We have to reach extraction beam power of 1 MW in RCS in the near future. Kicker impedance is most severe among other impedance sources. The matching resistor and newly developed diodes are connected at the power supply to reduce the impedance. We confirmed that reduced voltages and stable operation of accelerator.
Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3927 - 3929, 2012/05
The J-PARC rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) was heavily affected by the last Great East Japan Earthquake. The damage to each device was investigated and an attempt was made to restore them, with successful beam commissioning of the RCS beginning on 17th December 2011. On the 22nd, a 3 GeV beam was extracted to the MLF with beam currents that approached those obtained before the earthquake. Not only the recovery, but also an improvement of the RCS has been achieved, enabling high-power stable operation with low beam losses. Specifically, downstream beam losses due to the charge exchange foil were localized by installing a new collimator at injection area. As a result, the residual activation of this area was reduced by one order of magnitude and created the possibility of a higher beam power for the RCS. In a recent high-intensity trial of the RCS with a 420 kW equivalent intensity beam, significant progress toward design output beam power of 1 MW was demonstrated.
Saha, P. K.; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Tani, Norio; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Meigo, Shinichiro
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.490 - 492, 2012/05
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Kazami; Saha, P. K.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Hayashi, Naoki; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.2122 - 2124, 2012/05
Transverse beam halo is one of the most important beam parameters due to limit the performance of the high intensity beam accelerator. Therefore the transverse beam halo measurement is required to increase the beam power of the J-PARC 3-GeV RCS. In order to measure the transverse beam halo during the beam operation, halo monitors which are horizontal and vertical scanning aluminum plates type has been installed in the extraction beam line. But the residual secondary electrons hindered the beam halo diagnostic. We report how to take measures against the intrinsic issues of this monitor.